Conditions
Vertebrogenic Pain:
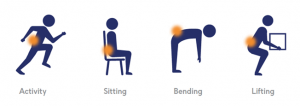
Vertebrogenic pain is a distinct type of chronic low back pain caused by damage to vertebral endplates, the tissue that covers the top and the bottom of each vertebral body and separates it from the disc. Disc degeneration, and the wear and tear that occurs with everyday living, produces stresses on the endplates that damage them, leading to inflammation and vertebrogenic pain. The basivertebral nerve (BVN), found within the vertebrae, carries pain signals from the inflamed endplates to the brain. Patients who find relief from the Intracept Procedure often describe pain in the middle of their low back that is made worse by physical activity, prolonged sitting, and bending forward or with bending and lifting.
Herniated Disk:
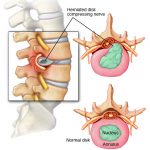
A slipped disc – known as a prolapsed or herniated disc – occurs when one of the discs that sit between the bones of the spine (the vertebrae) is damaged and presses on the nerves. This can cause back pain and neck pain, as well as symptoms such as numbness, a tingling sensation, or weakness in other areas of the body.
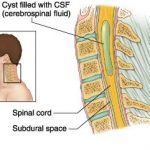
Subdural Hematoma:
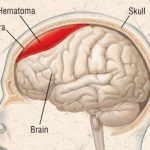
A subdural hematoma occurs when a blood vessel near the surface of the brain bursts. Blood builds up between the brain and the brain’s tough outer lining. The condition is also called a subdural hemorrhage
Brain Tumor:
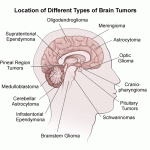
A brain tumor is an abnormal growth of tissue in the brain or central spine that can disrupt proper brain function. Doctors refer to a tumor based on where the tumor cells originated, and whether they are cancerous (malignant) or not (benign).
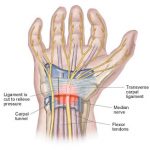
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome:
Carpal tunnel syndrome occurs when the median nerve, which runs from the forearm into the palm of the hand, becomes pressed or squeezed at the wrist. The median nerve controls sensations to the palm side of the thumb and fingers (although not the little finger), as well as impulses to some small muscles in the hand that allow the fingers and thumb to move.
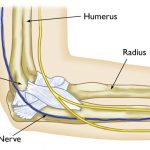
Ulnar Nerve Entrapment:
The condition is caused by compression or irritation of the ulnar nerve. It can cause numbness, tingling and/or pain in the arm and certain fingers.
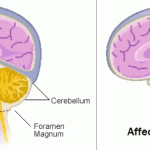
Chiari Malformations:
The condition in which brain tissue extends into your spinal canal. It occurs when part of your skull is abnormally small or misshapen, pressing on your brain and forcing it downward.
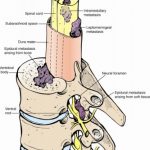
Spinal Cord Tumors:
A spinal tumor is a growth that develops within your spinal canal or within the bones of your spine. It may be cancerous or noncancerous.
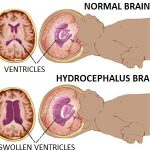
Hydrocephalus:
As the name implies, it is a condition in which the primary characteristic is excessive accumulation of fluid in the brain. Although hydrocephalus was once known as “water on the brain,” the “water” is actually cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) — a clear fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord.
Neck Pain:
Your neck is made up of vertebrae that extend from the skull to the upper torso. Cervical discs absorb shock between the bones. The bones, ligaments, and muscles of your neck support your head and allow for motion. Any abnormalities, inflammation, or injury can cause neck pain or stiffness.
Back Pain:
Lower back pain can be caused by a variety of problems with any parts of the complex, interconnected network of spinal muscles, nerves, bones, discs or tendons in the lumbar spine.
Spinal Deformity:
Spine deformity can happen when unnatural curvature occurs, as in scoliosis (side-to-side curvature) or kyphosis and Scheuermann’s disease (front-to-back curvature). It also occurs due to defect (e.g. spondylolisthesis) or damage to the spine (if there are multiple fractures or ankylosing spondylitis).
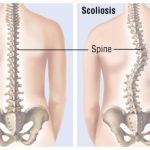
Adult Scoliosis:
Everyone’s spine has subtle natural curves. But some people have different curves, side-to-side spinal curves that also twist the spine. This condition is called “scoliosis”. On an x-ray with a front or rear view of the body, the spine of a person with scoliosis looks more like an “S” or a “C” than a straight line. These curves can make a person’s shoulders or waist appear uneven. These curves can’t be corrected simply by learning to stand up straight.
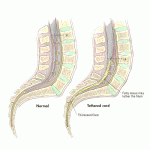
Tethered Spinal Cord:
Tethered spinal cord syndrome is a neurological disorder caused by tissue attachments that limit the movement of the spinal cord within the spinal column. These attachments cause an abnormal stretching of the spinal cord.
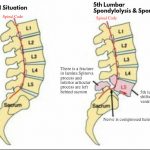
Spondylolisthesis:
Spondylolisthesis is a condition in which one of the bones of the spine (vertebrae) slips out of place onto the vertebra below it. If it slips too much, the bone might press on a nerve, causing pain. Usually, the bones of the lower back are affected
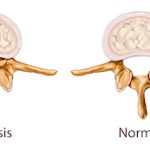
Spinal Stenosis:
Spinal stenosis is a narrowing of the open spaces within your spine, which can put pressure on your spinal cord and the nerves that travel through the spine to your arms and legs. Spinal stenosis occurs most often in the lower back and the neck.
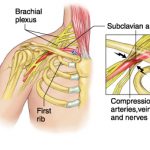
Thoracic Outlet Syndrome:
Thoracic outlet syndrome is a condition whereby symptoms are produced from compression of nerves or blood vessels, or both, because of an inadequate passageway through an area (thoracic outlet) between the base of the neck and the armpit.
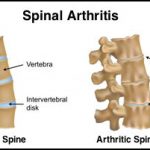
Arthritis of Spine:
Osteoarthritis of the spine is a breakdown of the cartilage of the joints and discs in the neck and lower back. Sometimes, osteoarthritis produces spurs that put pressure on the nerves leaving the spinal column. This can cause weakness and pain in the arms or legs.
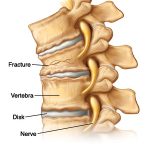
Spinal Fractures:
The type of fracture in the spine that is typically caused by osteoporosis is generally referred to as a compression fracture. A compression fracture is usually defined as a vertebral bone in the spine that has decreased at least 15 to 20% in height due to fracture.
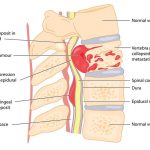
Spinal Cord Compression:
The spinal cord consists of nerves that send signals or messages back and forth between the brain and the rest of the body. Spinal cord compression occurs when a mass places pressure on the cord. A mass can include a tumor or bone fragment.